Pointer sets
This page has been automatically translated using the Google Translate API services. We are working on improving texts. Thank you for your understanding and patience.
Header
#include <core/setpt.h>
Functions
| SetPt(type)* | setpt_create (...) |
| void | setpt_destroy (...) |
| uint32_t | setpt_size (...) |
| type* | setpt_get (...) |
| const type* | setpt_get_const (...) |
| bool_t | setpt_insert (...) |
| bool_t | setpt_delete (...) |
| type* | setpt_first (...) |
| const type* | setpt_first_const (...) |
| type* | setpt_last (...) |
| const type* | setpt_last_const (...) |
| type* | setpt_next (...) |
| const type* | setpt_next_const (...) |
| type* | setpt_prev (...) |
| const type* | setpt_prev_const (...) |
| void | setpt_foreach (...) |
| void | setpt_foreach_const (...) |
| void | setpt_fornext (...) |
| void | setpt_fornext_const (...) |
| void | setpt_forback (...) |
| void | setpt_forback_const (...) |
| void | setpt_forprev (...) |
| void | setpt_forprev_const (...) |
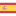
Just like we saw the ArrPt, the type SetPt are set-type containers (based on binary search trees) but they contain pointers instead of complete objects. Therefore, everything seen in Sets works, except for the need to create and free the memory occupied by each object, since in the container there will only be one pointer to the object (Figure 1). The decision to use SetSt or SetPt will depend on each case, but the reasons will be practically the same as those that conditioned the choice between ArrSt and ArrPt.
- If external references to elements are maintained, use
SetPt. - If we host opaque objects, use
SetPt.
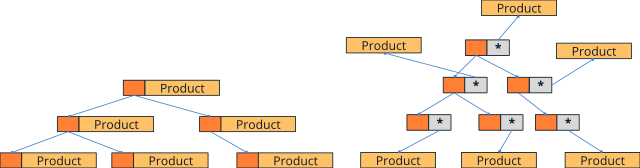
1. Create pointer sets
- Use setpt_create to create a set.
- Use setpt_destroy to destroy the set and its elements.
- Use setpt_insert to insert an element.
The main difference with respect to SetSt lies in the insertion and deletion of objects. This time setpt_insert() will not return the memory address of the inserted object, but rather a boolean indicating whether the insertion was possible or not (Listing 1). For its part, the destructor must free the memory of the object itself, in addition to the memory reserved by the object for each field.
char_t* as a key.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
typedef struct _product_t Product; struct _product_t { type_t type; String *code; String *desc; Image *image; real32_t price; }; static void i_destroy(Product **prod) { str_destroy(&(*prod)->code); str_destroy(&(*prod)->desc); image_destroy(&(*prod)->image); heap_delete(prod, Product); } static int i_compare(const Product *prod, const char_t *code) { return str_cmp(prod->code, code); } SetPt(Product) *products = setpt_create(i_compare, Product, char_t); ... Product *prod = heap_new(Product); prod->type = ekHDD; prod->code = str_c("GTK-1050"); prod->desc = str_c("Gigabyte GeForce GTX 1050 OC 2Gb GDDR5"); prod->image = load_image("card.png"); prod->price = 573.34; if (setpt_insert(products, "GTK-1050", prod, Product, char_t) == FALSE) { // Insert error i_destroy(&prod); } ... setpt_destroy(&products, i_destroy, Product); |
setpt_create ()
Create an empty pointer set.
SetPt(type)* setpt_create(FPtr_compare func_compare, type, ktype);
| func_compare | Function to compare element-key. |
| type | Object type. |
| ktype | Key type. |
Return
The new set.
Remarks
See Create pointer sets.
setpt_destroy ()
Destroy a set and all its elements.
void setpt_destroy(SetPt(type) **set, FPtr_destroy func_destroy, type);
| set | The set. Will be set to |
| func_destroy | Function to destroy an element of the set. If it is |
| type | Object type. |
setpt_size ()
Get the number of set elements.
uint32_t setpt_size(const SetPt(type) *set, type);
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Number of items.
setpt_get ()
Search for an item in O(logn). If it exists, the internal iterator will be set to it.
type* setpt_get(SetPt(type) *set, const ktype *key, type, ktype);
| set | The set. |
| key | Search key. |
| type | Object type. |
| ktype | Key type. |
Return
Pointer to the element if it exists, or NULL if not.
Remarks
See Search and tour in sets. Iterators.
setpt_get_const ()
Const version of setpt_get.
const type* setpt_get_const(const SetPt(type) *set, const ktype *key, type, ktype);
| set | The set. |
| key | Search key. |
| type | Object type. |
| ktype | Key type. |
Return
Element.
setpt_insert ()
Insert a new item in the set.
bool_t setpt_insert(SetPt(type) *set, const ktype *key, type *ptr, type, ktype);
| set | The set. |
| key | Key to insert. |
| ptr | Pointer to the element to insert. |
| type | Object type. |
| ktype | Key type. |
Return
TRUE if the item has been inserted. FALSE if another element with the same key already exists.
Remarks
Inserting or deleting elements invalidates the internal set iterator. You must initialize it with setpt_first or similar.
setpt_delete ()
Remove an item from the set.
bool_t setpt_delete(SetPt(type) *set, type *key, FPtr_destroy func_destroy, type, ktype);
| set | The set. |
| key | Key to delete. |
| func_destroy | Element destructor. Can be |
| type | Object type. |
| ktype | Key type. |
Return
TRUE if the item has been deleted, or FALSE if there is no item with that key.
Remarks
Inserting or deleting elements invalidates the internal set iterator. You must initialize it with setpt_first or similar.
setpt_first ()
Get the first element of the set and initialize the internal iterator.
type* setpt_first(SetPt(type) *set, type);
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Pointer to the first element or NULL if the set is empty.
Remarks
Ver Search and tour in sets. Iterators.
setpt_first_const ()
Const version of setpt_first.
const type* setpt_first_const(const SetPt(type) *set, type);
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Element.
setpt_last ()
Get the last element of the set and initialize the internal iterator.
type* setpt_last(SetPt(type) *set, type);
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Pointer to the last item or NULL if the set is empty.
Remarks
Ver Search and tour in sets. Iterators.
setpt_last_const ()
Const version of setpt_last.
const type* setpt_last_const(const SetPt(type) *set, type);
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Element.
setpt_next ()
Get the next set item, after increasing the internal iterator.
type* setpt_next(SetPt(type) *set, type);
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Pointer to the next item or NULL if the iterator has reached the last.
Remarks
Use setpt_first to initialize the internal iterator.
setpt_next_const ()
Const version of setpt_next.
const type* setpt_next_const(const SetPt(type) *set, type);
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Element.
setpt_prev ()
Gets the previous element of the set, after decrementing the internal iterator.
type* setpt_prev(SetPt(type) *set, type);
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Pointer to the previous item or NULL if the iterator has reached the first.
Remarks
Use setpt_last to initialize the internal iterator on reversed loops.
setpt_prev_const ()
Const version of setpt_prev.
const type* setpt_prev_const(const SetPt(type) *set, type);
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Element.
setpt_foreach ()
Loop over all the elements of the set. Use setpt_fornext to close the loop.
void setpt_foreach(type *elem, SetPt(type) *set, type);
| elem | Name of the variable 'element' within the loop. |
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
setpt_foreach_const ()
Const version of setpt_foreach.
void setpt_foreach_const(const type *elem, const SetPt(type) *set, type);
| elem | Element. |
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
setpt_fornext ()
Close the loop opened by setpt_foreach, increasing the internal iterator.
void setpt_fornext(type *elem, SetPt(type) *set, type);
| elem | Name of the variable 'element'. It must be the same as |
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
setpt_fornext_const ()
Const version of setpt_fornext.
void setpt_fornext_const(const type *elem, const SetPt(type) *set, type);
| elem | Element. |
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
setpt_forback ()
Loop over all the elements of the set in reverse order. Use setpt_forprev to close the loop.
void setpt_forback(type *elem, SetPt(type) *set, type);
| elem | Name of the variable 'element' within the loop. |
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
setpt_forback_const ()
Const version of setpt_forback.
void setpt_forback_const(const type *elem, const SetPt(type) *set, type);
| elem | Element. |
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
setpt_forprev ()
Close the loop opened by setpt_forback, decreasing the internal iterator.
void setpt_forprev(type *elem, SetPt(type) *set, type);
| elem | Name of the variable 'element'. It must be the same as |
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |
setpt_forprev_const ()
Const version of setpt_forprev.
void setpt_forprev_const(const type *elem, const SetPt(type) *set, type);
| elem | Element. |
| set | The set. |
| type | Object type. |