Pointer arrays
This page has been automatically translated using the Google Translate API services. We are working on improving texts. Thank you for your understanding and patience.
Header
#include <core/arrpt.h>
Functions
| ArrPt(type)* | arrpt_create (...) |
| ArrPt(type)* | arrpt_copy (...) |
| ArrPt(type)* | arrpt_read (...) |
| ArrPt(type)* | arrpt_read_ex (...) |
| void | arrpt_destroy (...) |
| void | arrpt_destopt (...) |
| void | arrpt_clear (...) |
| void | arrpt_write (...) |
| void | arrpt_write_ex (...) |
| uint32_t | arrpt_size (...) |
| type* | arrpt_get (...) |
| const type* | arrpt_get_const (...) |
| type* | arrpt_first (...) |
| const type* | arrpt_first_const (...) |
| type* | arrpt_last (...) |
| const type* | arrpt_last_const (...) |
| type** | arrpt_all (...) |
| const type** | arrpt_all_const (...) |
| void | arrpt_append (...) |
| void | arrpt_prepend (...) |
| void | arrpt_insert (...) |
| type** | arrpt_insert_n (...) |
| void | arrpt_join (...) |
| void | arrpt_delete (...) |
| void | arrpt_pop (...) |
| void | arrpt_sort (...) |
| void | arrpt_sort_ex (...) |
| uint32_t | arrpt_find (...) |
| type* | arrpt_search (...) |
| const type* | arrpt_search_const (...) |
| type* | arrpt_bsearch (...) |
| const type* | arrpt_bsearch_const (...) |
| void | arrpt_foreach (...) |
| void | arrpt_foreach_const (...) |
| void | arrpt_forback (...) |
| void | arrpt_forback_const (...) |
| void | arrpt_end (void) |
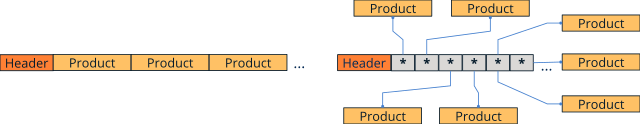
These containers are a specialization of arrays, where pointers to objects will be stored and not the objects themselves (Figure 1). Although, in general, everything seen in Arrays works, there are certain peculiarities that we must take into account:
- You have to create and free dynamic memory for each object.
- Access may be slower, since a pointer must be dereferenced for each element.
- Maintaining the array (inserting, deleting, sorting) can be faster since less memory has to be moved, especially in the case of handling large structures or arrays with many elements.
- The value
NULLcan be placed in any position. - It is safer if other parts of the application maintain pointers to the container elements.
- It is the only option to work with opaque objects.
1. Create pointer arrays
- Use arrpt_create to create an array.
- Use arrpt_destroy to destroy an array and its elements.
- Use arrpt_append to add a new pointer to the array.
- Use DeclPt to declare pointer types to
struct.
In (Listing 1) we see how to create and destroy arrays of Product pointers. The main difference with respect to object arrays lies in the management of the dynamic memory of each element.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
static void i_destroy(Product **product) { str_destroy(&(*product)->code); str_destroy(&(*product)->desc); image_destroy(&(*product)->image); heap_delete(product, Product); } ArrPt(Product) *products = arrpt_create(Product); Product *prod = heap_new(Product); arrpt_append(products, prod, Product); // Will modify the stored object prod->type = ekHDD; prod->code = str_c("GTK-1050"); prod->desc = str_c("Gigabyte GeForce GTX 1050 OC 2Gb GDDR5"); prod->image = load_image("card.png"); prod->price = 573.34; ... arrpt_destroy(&products, i_destroy, Product); |
2. Copying arrays of pointers
Use arrpt_copy to copy an array.
The copy works in a similar way as in Array copy, with the difference that we must dynamically reserve space for the object itself (Listing 2).
Product pointers.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
static Product *i_copy(const Product *src) { Product *dest = heap_new(Product); dest->type = src->type; dest->code = str_copy(src->code); dest->desc = str_copy(src->desc); dest->image = image_copy(src->image); dest->price = src->price; return dest; } ArrSt(Product) *nproducts = arrpt_copy(products, i_copy, Product); ... arrpt_destroy(&nproducts, i_destroy, Product); |
arrpt_create ()
Create an empty array of pointers.
ArrPt(type)* arrpt_create(type);
| type | Object type. |
Return
The new array.
arrpt_copy ()
Create a copy of an array of pointers.
ArrPt(type)* arrpt_copy(const ArrPt(type) *array, FPtr_copy func_copy, type);
| array | The original array. |
| func_copy | Object copy function. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
The copy of the original array.
Remarks
The copy function must create a dynamic object and allocate memory for internal fields that require it. If we pass NULL, a copy of the original pointers will be made, which can pose an integrity risk since the same object can be destroyed twice if we are not careful. See Copying arrays of pointers.
arrpt_read ()
Create an array by reading its contents from a Streams (de-serialization).
ArrPt(type)* arrpt_read(Stream *stream, FPtr_read func_read, type);
| stream | A read stream. |
| func_read | Constructor to create an object from the data obtained from a stream. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
The array readed.
arrpt_read_ex ()
Create an array by reading its contents from a Streams. The read function accepts data from the user.
ArrPt(type)* arrpt_read_ex(Stream *stream, FPtr_read func_read_ex, dtype *data, type, dtype);
| stream | A read stream. |
| func_read_ex | Constructor to create an object from the data obtained from a stream. |
| data | User data. |
| type | Object type. |
| dtype | Type of user data. |
Return
The array readed.
arrpt_destroy ()
Destroy an array and all its elements.
void arrpt_destroy(ArrPt(type) **array, FPtr_destroy func_destroy, type);
| array | The array. It will be set to |
| func_destroy | Function to destroy an element. If |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_destopt ()
Destroy an array and all its elements, as long as the array object is not NULL.
void arrpt_destopt(ArrSt(type) **array, FPtr_destroy func_destroy, type);
| array | The array. |
| func_destroy | See arrpt_destroy. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_clear ()
Delete the contents of the array, without destroying the container that will be left with zero elements.
void arrpt_clear(ArrPt(type) *array, FPtr_destroy func_destroy, type);
| array | The array. |
| func_destroy | Destructor function. See arrpt_destroy. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_write ()
Write an array in a Streams.
void arrpt_write(Stream *stream, const ArrPt(type) *array, FPtr_write func_write, type);
| stream | A write stream. |
| array | The array. |
| func_write | Function that writes the content of an element in a stream. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_write_ex ()
Write an array in a Streams. Write function accepts user data.
void arrpt_write_ex(Stream *stream, const ArrPt(type) *array, FPtr_write_ex func_write, const dtype *data, type, dtype);
| stream | A write stream. |
| array | The array. |
| func_write | Function that writes the content of an element in a stream. |
| data | Datos del usuario. |
| type | Object type. |
| dtype | Type of user data. |
arrpt_size ()
Get the number of elements in an array.
uint32_t arrpt_size(const ArrPt(type) *array, type);
| array | The array. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Number of elements.
arrpt_get ()
Get a pointer to the item in pos position.
type* arrpt_get(ArrPt(type) *array, const uint32_t pos, type);
| array | The array. |
| pos | Item position or index. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Item Pointer.
arrpt_get_const ()
Get a const pointer to the item in pos position.
const type* arrpt_get_const(const ArrPt(type) *array, const uint32_t pos, type);
| array | The array. |
| pos | Item position or index. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Item Pointer.
arrpt_first ()
Get a pointer to the first element of the array.
type* arrpt_first(ArrPt(type) *array, type);
| array | The array. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Item Pointer.
arrpt_first_const ()
Get a const pointer to the first element of the array.
const type* arrpt_first_const(const ArrPt(type) *array, type);
| array | The array. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Item Pointer.
arrpt_last ()
Get a pointer to the last element of the array.
type* arrpt_last(ArrPt(type) *array, type);
| array | The array. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Item Pointer.
arrpt_last_const ()
Get a const pointer to the last element of the array.
const type* arrpt_last_const(const ArrPt(type) *array, type);
| array | The array. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Item Pointer.
arrpt_all ()
Get a pointer to the internal memory of the array, which gives access to all the elements.
type** arrpt_all(ArrPt(type) *array, type);
| array | The array. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Base pointer. Increasing it one by one we will iterate over the elements.
Remarks
Use arrpt_foreach to iterate over all elements in a more secure and elegant way.
arrpt_all_const ()
Get a const pointer to the internal memory of the array, which gives access to all the elements.
const type** arrpt_all_const(const ArrPt(type) *array, type);
| array | The array. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Base pointer. Increasing it one by one we will iterate over the elements.
Remarks
Use arrpt_foreach_const to iterate over all elements in a more secure and elegant way.
arrpt_append ()
Adds a pointer to the end of the array.
void arrpt_append(ArrPt(type) *array, type *value, type);
| array | The array. |
| value | Pointer to the item to append. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_prepend ()
Insert a pointer at the beginning of the array. The rest of the elements will be shifted to the right.
void arrpt_prepend(ArrPt(type) *array, type *value, type);
| array | The array. |
| value | Pointer to the element to insert. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_insert ()
Insert a pointer in an arbitrary array position.
void arrpt_insert(ArrPt(type) *array, const uint32_t pos, type *value, type);
| array | The array. |
| pos | Position where it will be inserted. The current item in |
| value | Pointer to the element to insert. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_insert_n ()
Inserts several pointers at an arbitrary position in the array.
type** arrpt_insert_n(ArrPt(type) *array, const uint32_t pos, const uint32_t n, type);
| array | The array. |
| pos | Position where the first element will be inserted. The current element in |
| n | Number of elements to insert. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
Pointer to the first inserted pointer.
Remarks
The inserted pointers will be initialized to NULL.
arrpt_join ()
Join two vectors. Add all the elements of src to the end of dest.
void arrpt_join(ArrPt(type) *dest, const ArrPt(type) *src, FPtr_copy func_copy, type);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
ArrPt(Product) *products = create_products(...); ArrPt(Product) *new_products = new_products(...); // Join without 'copy' func. Dynamic 'Product' objects will be reused. arrpt_join(products, new_products, NULL, Product); arrpt_destroy(&new_products, NULL, Product); ... arrpt_destroy(&products, i_destroy, Product); // Join with 'copy' func. Dynamic 'Product' objects will be duplicate. arrpt_join(products, new_products, i_copy, Product); arrpt_destroy(&new_products, i_destroy, Product); ... arrpt_destroy(&products, i_destroy, Product); |
| dest | The destination array. |
| src | The array whose elements will be added to |
| func_copy | Object copy function. |
| type | Object type. |
Remarks
The copy function must create dynamic memory for both the object and the fields that require it. If it is NULL it will only add a copy of the original pointer to dest.
arrpt_delete ()
Remove a pointer from the array.
void arrpt_delete(ArrPt(type) *array, const uint32_t pos, FPtr_destroy func_destroy, type);
| array | The array. |
| pos | Position of the item to be deleted. The current item in |
| func_destroy | Element destructor. See arrpt_destroy. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_pop ()
Remove the last pointer from the array.
void arrpt_pop(ArrPt(type) *array, FPtr_destroy func_destroy, type);
| array | The array. |
| func_destroy | Element destructor. See arrpt_destroy. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_sort ()
Sort the array elements using Quicksort.
void arrpt_sort(ArrPt(type) *array, FPtr_compare func_compare, type);
| array | The array. |
| func_compare | Function to compare two elements. Sort and search in arrays. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_sort_ex ()
Sort array elements using Quicksort and additional data.
void arrpt_sort_ex(ArrPt(type) *array, FPtr_compare_ex func_compare, type, dtype);
| array | The array. |
| func_compare | Function to compare two elements using an additional data. |
| type | Object type. |
| dtype | Type of data in the comparison function. |
arrpt_find ()
Search for a specific pointer in the array.
uint32_t arrpt_find(const ArrPt(type) *array, type *elem, type);
| array | The array. |
| elem | Pointer to find. |
| type | Object type. |
Return
The position of the pointer if it exists, or UINT32_MAX if not.
arrpt_search ()
Search for an element in the array linearly O(n).
type* arrpt_search(ArrPt(type) *array, FPtr_compare func_compare, ktype key, uint32_t *pos, type, ktype);
| array | The array. |
| func_compare | Comparison function. The first parameter is the element, the second the search key. Sort and search in arrays. |
| key | Search key. Pointer to a data type that may be different from the type of array element. |
| pos | Position of the element in the array (if it exists), or |
| type | Object type. |
| ktype | Key type. |
Return
Pointer to the first element that matches the search criteria or NULL if none exists.
arrpt_search_const ()
Const version of arrpt_search.
const type* arrpt_search_const(const ArrPt(type) *array, FPtr_compare func_compare, const ktype *key, uint32_t *pos, type, ktype);
| array | The array. |
| func_compare | Comparison function. |
| key | Search key. |
| pos | Position of the element in the array. |
| type | Object type. |
| ktype | Key type. |
Return
Element.
arrpt_bsearch ()
Search for an element in the array logarithmically O(logn).
type* arrpt_bsearch(ArrPt(type) *array, FPtr_compare func_compare, ktype key, uint32_t *pos, type, ktype);
| array | The array. |
| func_compare | Comparison function. The first parameter is the element, the second the search key. Sort and search in arrays. |
| key | Key to search. Pointer to a data type that can be different from the element type of the array. |
| pos | Position of the element in the array (if it exists), or |
| type | Object type. |
| ktype | Key type. |
Return
Pointer to the first element that matches the search criteria or NULL if none exists.
Remarks
The array must be sorted according to the same criteria as the search. If not, the result is unpredictable.
arrpt_bsearch_const ()
Const version of arrpt_bsearch.
const type* arrpt_bsearch_const(const ArrPt(type) *array, FPtr_compare func_compare, const ktype *key, uint32_t *pos, type, ktype);
| array | The array. |
| func_compare | Comparison function. |
| key | Search key. |
| pos | Position of the element in the array. |
| type | Object type. |
| ktype | Key type. |
Return
Element.
arrpt_foreach ()
Iterate on all array elements. Uses arrpt_end to close the loop.
void arrpt_foreach(type *elem, ArrPt(type) *array, type);
1 2 3 |
arrpt_foreach(product, array, Product) bstd_printf("Index:%d, Id:%d\n", product_i, product->id); arrpt_end() |
| elem | Name of the 'element' variable within the loop. Adding the suffix |
| array | The array. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_foreach_const ()
Const version of arrpt_foreach.
void arrpt_foreach_const(const type *elem, const ArrPt(type) *array, type);
| elem | Element. |
| array | The array. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_forback ()
Iterate on all array elements backward, from the last to the first. Uses arrpt_end to close the loop.
void arrpt_forback(type *elem, ArrPt(type) *array, type);
1 2 3 4 |
// Now in reverse order arrpt_forback(product, array, Product) bstd_printf("Index:%d, Id:%d\n", product_i, product->id); arrpt_end() |
| elem | Name of the 'element' variable within the loop. Adding the suffix |
| array | The array. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_forback_const ()
Const version of arrpt_forback.
void arrpt_forback_const(const type *elem, const ArrPt(type) *array, type);
| elem | Element. |
| array | The array. |
| type | Object type. |
arrpt_end ()
Close the loop opened by arrpt_foreach, arrpt_foreach_const, arrpt_forback or arrpt_forback_const.
void
arrpt_end(void);