Colors
This page has been automatically translated using the Google Translate API services. We are working on improving texts. Thank you for your understanding and patience.
Functions
| color_t | color_rgb (...) |
| color_t | color_rgba (...) |
| color_t | color_rgbaf (...) |
| color_t | color_hsbf (...) |
| color_t | color_red (...) |
| color_t | color_green (...) |
| color_t | color_blue (...) |
| color_t | color_gray (...) |
| color_t | color_bgr (...) |
| color_t | color_html (...) |
| void | color_to_hsbf (...) |
| void | color_to_html (...) |
| void | color_get_rgb (...) |
| void | color_get_rgbf (...) |
| void | color_get_rgba (...) |
| void | color_get_rgbaf (...) |
| uint8_t | color_get_alpha (...) |
| color_t | color_set_alpha (...) |
Types and Constants
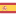
The colors in Draw2D are encoded using a 32-bit integer with the four RGBA channels in Little-Endian: Red in byte 0, green in 1, blue in 2 and alpha (or transparency) in 3 (Figure 1). The alias color_t is used as an equivalent to uint32_t. In the particular case that byte 3 is equal to 0 (fully transparent), the first three bytes will not contain RGB information, but an index with a special color.
- Use color_rgba to create a color using its RGBA components.
- Use color_get_rgba to get the RGBA components.
- Use color_html to translate an string into HTML format (
"#RRGGBB"). - Use kCOLOR_BLACK and others to access predefined basic colors.
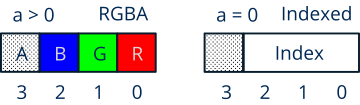
1. HSV space
RGB representation is based on the addition of the three primary light colors. It is the most widespread within the generation of computer images, especially when calculating shading and reflections. It is also used in TV, monitors or projectors where each pixel is obtained by combining the light of three emitters. However, it is very unintuitive for human color editing. For example, given a color in RGB, it is very difficult to increase the brightness or vary the tone (between red and orange, for example) by manipulating the triplet (r, g, b). The HSV space (Hue, Saturation, Value) also called HSB (Brightness) solves this problem, since the effect of altering this group of values will be highly predictable (Figure 2).
- Use color_hsbf to create an RGB color from its components H, S, B.
- Use color_to_hsbf to get the H, S, B components.
- Hue: Continuous cyclical value between 0 and 1. Where
0=Red,1/3=Green,2/3=Blue,1=Red (Table 1). - Saturation: It is equivalent to adding white paint to the base tone. When
S=1no white is added (maximum saturation, pure color). But ifS=0we will have a pure white, regardless of the tone. - Brightness: It is equivalent to adding black paint to the
HScombination. IfB=1no black is added (maximum brightness). IfB=0we will have a pure black, regardless of the hue and saturation.
| RGB | HSV | ||
| (0,0,0) |  |
kCOLOR_BLACK |
(?,?,0) |
| (1,1,1) |  |
kCOLOR_WHITE |
(?,0,1) |
| (1,0,0) | 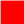 |
kCOLOR_RED |
(0,1,1) |
| (1,1,0) |  |
kCOLOR_YELLOW |
(1/6,1,1) |
| (0,1,0) |  |
kCOLOR_GREEN |
(1/3,1,1) |
| (0,1,1) |  |
kCOLOR_CYAN |
(1/2,1,1) |
| (0,0,1) |  |
kCOLOR_BLUE |
(2/3,1,1) |
| (1,0,1) |  |
kCOLOR_MAGENTA |
(5/6,1,1) |
Unlike RGB, HSVs are not totally independent. As we reduce the brightness, the number of colors of the same tone will decrease until we reach B=0 where we will have pure black regardless of H and S. On the other hand, if S=0 H will be overridden and we will have the different shades of gray as B changes from 0 (black) to 1 (white).
kCOLOR_TRANSPARENT
const color_t kCOLOR_TRANSPARENT;
Totally transparent color, absence of color or null color.
kCOLOR_DEFAULT
const color_t kCOLOR_DEFAULT;
Default color.
kCOLOR_BLACK
const color_t kCOLOR_BLACK;
BLACK color rgb(0,0,0).
kCOLOR_WHITE
const color_t kCOLOR_WHITE;
WHITE color rgb(255,255,255).
kCOLOR_RED
const color_t kCOLOR_RED;
RED color rgb(255,0,0).
kCOLOR_GREEN
const color_t kCOLOR_GREEN;
GREEN color rgb(0,255,0).
kCOLOR_BLUE
const color_t kCOLOR_BLUE;
BLUE color rgb(0,0,255).
kCOLOR_YELLOW
const color_t kCOLOR_YELLOW;
YELLOW color rgb(255,255,0).
kCOLOR_CYAN
const color_t kCOLOR_CYAN;
CYAN color rgb(0,255,255).
kCOLOR_MAGENTA
const color_t kCOLOR_MAGENTA;
MAGENTA color rgb(255,0,255).
color_rgb ()
Create a color from the channels R (red), G (green) y B (blue).
color_t color_rgb(const uint8_t r, const uint8_t g, const uint8_t b);
| r | Red channel. |
| g | Green channel. |
| b | Blue channel. |
Return
Color.
Remarks
The alpha channel is set to 255 (totally opaque).
color_rgba ()
Create a color from the channels R (red), G (green), B (blue) and A (alpha).
color_t color_rgba(const uint8_t r, const uint8_t g, const uint8_t b, const uint8_t a);
| r | Red channel. |
| g | Green channel. |
| b | Blue channel. |
| a | Alpha channel (transparency). |
Return
Color.
Remarks
a=0 not supported. Use kCOLOR_TRANSPARENT in those cases.
color_rgbaf ()
Create a color from the normalized RGBA channels from 0 to 1.
color_t color_rgbaf(const real32_t r, const real32_t g, const real32_t b, const real32_t a);
| r | Red channel. |
| g | Green channel. |
| b | Blue channel. |
| a | Alpha channel (transparency). |
Return
Color.
Remarks
a=0 not supported. Use kCOLOR_TRANSPARENT in those cases.
color_hsbf ()
Creates a color (rgb) from its components Hue-Saturation-Brightness.
color_t color_hsbf(const real32_t hue, const real32_t sat, const real32_t bright);
| hue | Hue component. |
| sat | Saturation component. |
| bright | Brightness component. |
Return
Color.
color_red ()
Create an RGB color using only the red channel.
color_t color_red(const uint8_t r);
| r | Red Channel. |
Return
Color.
Remarks
Equivalent to color_rgb(r, 0, 0).
color_green ()
Create an RGB color using only the green channel.
color_t color_green(const uint8_t g);
| g | Green channel. |
Return
Color.
Remarks
Equivalent to color_rgb(0, g, 0).
color_blue ()
Create an RGB color using only the blue channel.
color_t color_blue(const uint8_t b);
| b | Blue channel. |
Return
Color.
Remarks
Equivalent to color_rgb(0, 0, b).
color_gray ()
Creates a gray RGB color from intensity value.
color_t color_gray(const uint8_t l);
| l | Intensity (luminance). |
Return
Color.
Remarks
Equivalent to color_rgb(l, l, l).
color_bgr ()
Create a color from a 32-bit BGR value. Byte 0 corresponds to channel B , 1 to G and 2 to R. The highest order byte is ignored (set to 255).
color_t color_bgr(const uint32_t bgr);
| bgr | The bgr 32bits value. |
Return
Color.
Remarks
This byte order is typical in Web colors.
color_html ()
Create a color from a string in HTML or CSS format.
color_t color_html(const char_t *html);
1 2 |
color_t c1 = color_html("#FF0000"); // Red color_t c2 = color_html("#000080"); // Navy |
| html | The text string with the HTML color. |
Return
The color transformed to RGB.
color_to_hsbf ()
Convert a color (rgb) to HSB space (hue, saturation, brightness).
void color_to_hsbf(const color_t color, real32_t *hue, real32_t *sat, real32_t *sat);
| color | Color. |
| hue | Hue component. |
| sat | Saturation component. |
| sat | Brightness component. |
color_to_html ()
Convert a color to the HTML or CSS format (#RRGGBB).
void color_to_html(const color_t color, char_t *html, const uint32_t size);
| color | The color to convert. |
| html | Buffer where to write the result. |
| size | Result buffer size. |
color_get_rgb ()
Returns RGB color values.
void color_get_rgb(const color_t color, uint8_t *r, uint8_t *g, uint8_t *b);
| color | Color. |
| r | Red channel. |
| g | Green channel. |
| b | Blue channel. |
Remarks
In system or indexed colors, it makes effective the RGB value.
color_get_rgbf ()
Returns RGB color values, normalized from 0 to 1.
void color_get_rgbf(const color_t color, real32_t *r, real32_t *g, real32_t *b);
| color | Color. |
| r | Red channel. |
| g | Green channel. |
| b | Blue channel. |
Remarks
In system or indexed colors, it makes effective the RGB value.
color_get_rgba ()
Returns the RGBA values of the color.
void color_get_rgba(const color_t color, uint8_t *r, uint8_t *g, uint8_t *b, uint8_t *a);
| color | Color. |
| r | Red channel. |
| g | Green channel. |
| b | Blue channel. |
| a | Alpha channel (transparency). |
Remarks
In system or indexed colors, it makes effective the RGBA value.
color_get_rgbaf ()
Returns the RGBA values of the color, normalized from 0 to 1.
void color_get_rgbaf(const color_t color, real32_t *r, real32_t *g, real32_t *b, real32_t *a);
| color | Color. |
| r | Red channel. |
| g | Green channel. |
| b | Blue channel. |
| a | Alpha channel (transparency). |
Remarks
In system or indexed colors, it makes effective the RGBA value.
color_get_alpha ()
Get the alpha (transparency) color component.
uint8_t color_get_alpha(const color_t color);
| color | Color. |
Return
The alpha component. If it is equal 0 it means that the color is indexed (does not contain RGB values).
color_set_alpha ()
Changes the alpha (transparency) value of a color.
color_t color_set_alpha(const color_t color, const uint8_t alpha);
| color | Color. |
| alpha | Alpha component. |
Return
The new color, with the altered alpha component.