Events
This page has been automatically translated using the Google Translate API services. We are working on improving texts. Thank you for your understanding and patience.
Functions
| Listener* | listener (...) |
| void | listen (void) |
| void | listener_destroy (...) |
| void | listener_update (...) |
| void | listener_event (...) |
| void | listener_pass_event (...) |
| uint32_t | event_type (...) |
| type* | event_sender (...) |
| type* | event_params (...) |
| type* | event_result (...) |
An event is an action that occurs during the program execution, usually asynchronously or unpredictably and on which a given object must be notified. In applications with a graphical interface, many events are constantly occurring when the user interacts with the different controls. However, they can also occur in console applications, for example, when finish the writing of a file to disk or when downloading a page from Internet. In a system of events two actors intervene: The sender, which has evidence when the action occurs and the receiver who is notified that such action has occurred. To connect both ends we must perform these simple steps (Listing 1) (Figure 1):
- Create a listener indicating the receiving object and the callback function to which the sender should call.
- Said listener is assigned to the sender by the appropriate method. For example, the Button type provide the method button_OnClick to notify of a click.
- When the event occurs, the sender calls the callback function, indicating the receiving object (parameter of
listener) and detailed information about the event collected in the object Event.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
static void OnClick(AppCtrl *ctrl, Event *event) { // TODO: Response to click } ... void CreateButton(AppCtrl *ctrl) { Button *button = button_push(); button_text(button, "Ok"); button_OnClick(button, listener(ctrl, OnClick, AppCtrl)); } |
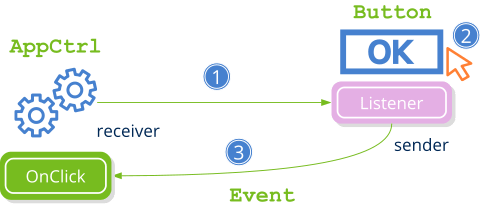
OnClick event.Events are used in bulk in GUI applications, but can also be useful in command line applications. See for example hfile_dir_loop in File operations.
listener ()
Create a listener. This function will link an event sender with the receiver, usually the application controller. The sender object is responsible for destroying the listener.
Listener* listener(type *obj, FPtr_event_handler func_event_handler, type);
| obj | Receiver object that will be passed as the first parameter to |
| func_event_handler | Callback function that will be called when the event occurs. Also known as event handler. |
| type | The type of receiver object. |
Return
Listener object.
listen ()
Like listener, but used in C++ to define class callbacks. Use of C++.
void
listen(void);
listener_destroy ()
Destroy a listener.
void listener_destroy(Listener **listener);
| listener | Listener. Will be set to |
Remarks
The sender is responsible for destroying the listener.
listener_update ()
Update the receiver and event handler. It is equivalent to destroying it, and creating it again.
void listener_update(Listener **listener, Listener *new_listener);
| listener | The current listener. |
| new_listener | The new listener. |
Remarks
This method must be used within the sender.
listener_event ()
Launches an event from the sender to the receiver.
void listener_event(Listener *listener, const uint32_t type, sender_type *sender, params_type *params, result_type *result, sender_type, params_type, result_type);
| listener | List through which the event will be sent. |
| type | Event code. |
| sender | Event sender. |
| params | Event parameters, or |
| result | Event result, or |
| sender_type | Type of sender object. |
| params_type | Type of params object, or |
| result_type | Type of result object, or |
Remarks
This method must be invoked within the event sender.
listener_pass_event ()
Pass the received event to another object, changing only the sender. Useful for not generating a new Event object.
void listener_pass_event(Listener *list, Event *event, sender_type *sender, sender_type);
| list | List through which the event will be resent. |
| event | Incoming event. |
| sender | The new event sender. |
| sender_type | Sender object type. |
Remarks
This method must be invoked within the event sender.
event_type ()
Get the event type.
uint32_t event_type(const Event *event);
| event | Event. |
Return
The event type. Normally associated with a enum. Examples in core_event_t, gui_event_t.
event_sender ()
Get the event sender.
type* event_sender(Event *event, type);
| event | Event. |
| type | Sender type. |
Return
Sender.
event_params ()
Get the event parameters, encapsulated in a structure, which will be different depending on the event type.
type* event_params(Event *event, type);
| event | Event. |
| type | Parameters type. |
Return
Event parameters.
event_result ()
Gets an object to write the results of the event. Some events require the return of data by the receiver. The type of result object will depend on the type of event.
type* event_result(Event *event, type);
| event | Event. |
| type | Result type. |
Return
Event results.